Health
Thyroid eye disease – Symptoms, causes, and management
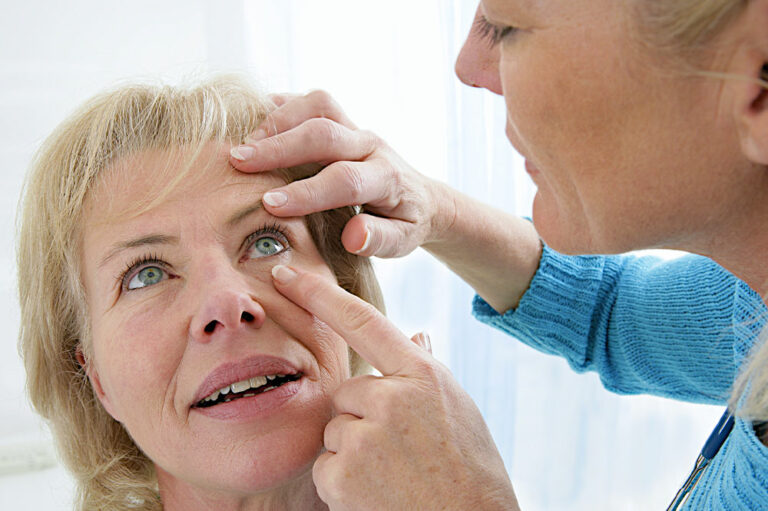
Thyroid eye disease, also popularly known as Grave’s disease, is an autoimmune condition in which specific eye muscles and tissues become inflamed. An autoimmune response causes inflammation, as the body attacks its own tissues when it perceives a threat. Grave’s or thyroid eye disease is categorized by swelling around the eyelids, bulged eyes, blurry vision, and vision impairment of varying degrees if not managed on time. Here are a few things to know about this condition: Symptoms There are a few common signs that help professionals diagnose thyroid eye disease. These are as follows: Changes in the eyes The condition is characterized by the swelling of the tissues and muscles in and around the eyes. As a result, patients may experience swelling around the eyelids, bloodshot eyes, and undereye bags. Additionally, all these symptoms make the eyes appear disproportionately huge and bulgy. The pupils also appear smaller in comparison to the rest of the eyes. Low tolerance of bright lights The inflammation and swelling of one’s eye muscles also cause muscle weakness. As a result, all the various parts of a person’s eyes, such as the cornea and iris, become more strained when an individual with this condition stares at bright lights.
Read More